Acerca del mecanizado CNC
Apr 11, 2025
¿Qué es el mecanizado CNC?
CNC significa Control Numérico por Computadora, por lo que el mecanizado CNC se puede definir como un proceso de fabricación donde un código computacional controla los parámetros del proceso, incluyendo:
Movimiento del cabezal de la máquina herramienta.
Movimiento de la pieza o avance.
Velocidad de rotación.
Selección de herramientas, para cabezales multiherramienta.
Cantidad de refrigerante si es necesario.
En palabras simples, significa utilizar el poder computacional para controlar y monitorear todos los movimientos necesarios de una máquina para fabricar piezas a partir de materia prima.
¿Cómo funciona el mecanizado CNC?
Básicamente, el programa CNC proporciona comandos que la máquina puede leer y comprender. Estos comandos indican a los motores de la máquina cuándo y cómo mover los componentes correspondientes para lograr los resultados deseados.
Las primeras máquinas CNC utilizaban tarjetas perforadas con el código escrito y tenían una flexibilidad limitada para el movimiento de la herramienta.
Sin embargo, las máquinas CNC actuales pueden asociarse con software CAD/CAM (Diseño Asistido por Computadora/Fabricación Asistida por Computadora). Esto significa que el diseñador puede crear un modelo 3D de la pieza y luego traducir sus parámetros a un programa CNC mediante el software CAM.
Este programa final, creado por el software CAM, se introduce en la máquina y comienza el proceso de fabricación. La pieza está terminada cuando la máquina termina de ejecutar el programa.
Otro aspecto importante de las actuales y más sofisticadas máquinas CNC es la flexibilidad que tienen, ya que pueden moverse en un rango de 2,5 ejes, 3 ejes o 5 ejes dependiendo del tipo de máquina.
Mecanizado CNC para maderaAunque muchos podrían pensar que la ebanistería es un arte reservado para los talladores más hábiles, lo cierto es que el mecanizado CNC para madera permite un trabajo más eficiente, incluso para los diseños más complejos.
Con el mecanizado CNC para madera es posible producir piezas más grandes en menos tiempo. Además, permite al carpintero conservar la belleza natural y la resistencia de la madera, algo difícil de conseguir con otras máquinas para el procesamiento de madera.
Otros beneficios del uso del mecanizado CNC para madera son:
Las formas complejas que son demasiado difíciles para el trabajo manual se pueden lograr fácilmente.
Mayor precisión y tiempos de producción más cortos.
Mayor eficiencia y menor desperdicio de material.
Mayor rentabilidad.
Mecanizado CNC para la industria médicaEs bien sabido que la industria médica es muy exigente y debe cumplir con todos los estándares. Este es el caso del mecanizado CNC para la industria médica.
Afortunadamente, como se mencionó anteriormente, los principales beneficios del mecanizado CNC son la alta eficiencia y la alta precisión que casi no dejan margen de error.
Esto convierte al mecanizado CNC en la mejor opción de fabricación para la industria médica, siendo el mecanizado de precisión la alternativa elegida para cumplir con los estrictos requisitos de tolerancia. Otros requisitos comunes incluyen:
Geometrías complejas que normalmente requieren máquinas de 5 ejes.
Niveles muy altos de limpieza.
Posibilidad de mecanizar diferentes materiales especiales.
Acabado superficial de primer nivel.
Las aplicaciones comunes del mecanizado CNC para la industria médica incluyen:
Implantes y prótesis.
Instrumentos quirúrgicos.
Componentes electrónicos para equipos médicos.
Microdispositivos médicos que requieren micromaquinado.
Mecanizado CNC para fundiciónLa fundición es un proceso de fabricación que requiere buenos moldes para obtener los resultados deseados. Esto significa que es necesario seleccionar el mejor proceso para producir los moldes.
El mecanizado CNC para fundición en máquinas de 5 ejes reduce la posibilidad de error al mover la pieza fundida entre operaciones de mecanizado. Esta reducción de errores permite que la pieza cumpla con las tolerancias más estrictas.
Otra buena aplicación del mecanizado CNC para fundición es que la mayoría de las piezas fundidas requieren un posprocesamiento para mejorar el acabado superficial. El mecanizado CNC para fundición permite lograr el acabado superficial deseado de forma rápida y eficiente.
Además, el mecanizado CNC puede manejar el tipo de materiales que se utilizan comúnmente para fundiciones, como el aluminio, lo que puede ser un problema para otros procesos de fabricación..
Mecanizado CNC para aluminio
Al ser un metal ligero, el aluminio es el material preferido para muchas aplicaciones, siendo las más utilizadas la automoción y la industria aeroespacial. Sin embargo, su uso en algunas de estas aplicaciones requiere formas muy complejas.
Además, pueden requerirse piezas delgadas, lo que aumenta la posibilidad de deformación debido a la baja dureza y la alta expansión térmica del material.
Aquí es donde el mecanizado CNC para aluminio cobra importancia. El mecanizado CNC de 5 ejes para aluminio ofrece ventajas como:
Es fácil de configurar, lo que reduce los plazos de entrega y mejora la eficiencia.
Permite trabajar con geometría compleja gracias a la capacidad de evitar la colisión con el portaherramientas al inclinar la mesa de wok o la herramienta de corte.
Se pueden utilizar herramientas más cortas y rígidas, algunas con altas velocidades de husillo, lo que se consigue reduciendo la carga en la herramienta de corte.
Las piezas no tienen que pasar por diferentes estaciones de trabajo, lo que significa que se reducen los errores, aumenta la precisión y se garantiza la calidad.
Estas máquinas pueden utilizar otras alternativas como el corte por chorro de agua o el corte láser que eliminan los problemas de trabajar con piezas de aluminio muy delgadas.
Mecanizado CNC para piezas aeroespaciales
Con la cantidad de componentes necesarios para ensamblar un avión y la complejidad de dichos componentes, está claro que la industria aeroespacial requiere la mayor precisión y eficiencia posibles en un proceso de fabricación.
Por lo tanto, el mecanizado CNC para piezas aeroespaciales ha crecido en popularidad y ahora es la opción preferida para la fabricación de componentes aeroespaciales.
El mecanizado CNC para piezas aeroespaciales debe abordar requisitos complejos como:
Trabajando con paredes delgadas.
Limitar la deformación del material, por ejemplo, al trabajar con aluminio y otros materiales ligeros.
Trabajando con geometrías curvas y complejas.
Por otro lado, el mecanizado CNC es la mejor opción para la producción de piezas aeroespaciales ya que proporciona los siguientes beneficios:
Es un proceso rentable.
Puede proporcionar resultados de alta calidad.
Puede trabajar con diseños personalizados.
Proporciona ingeniería de alta precisión y exactitud.
Reduce y a veces elimina el error humano.
Puede producir geometrías complejas.
Mecanizado CNC para joyería
En el pasado, las joyas solo se elaboraban a mano por artesanos de renombre. Sin embargo, esto ya no es así, ya que cada vez más productores de joyas implementan métodos para mejorar su eficiencia y aumentar su rentabilidad.
El mecanizado CNC para joyería ofrece diversas ventajas para los artesanos y fabricantes de joyas en general. Las ventajas más comunes son:
Crea fácilmente modelos maestros para fundir las joyas.
Cree rápidamente moldes de fundición con gran precisión.
Cree finas joyas de uso final cuando utilice sofisticadas máquinas CNC.
Cree grabados personalizados de forma rápida y precisa.
Acabado sencillo de las joyas con procesos de facetado de mármol y pulido de joyas.
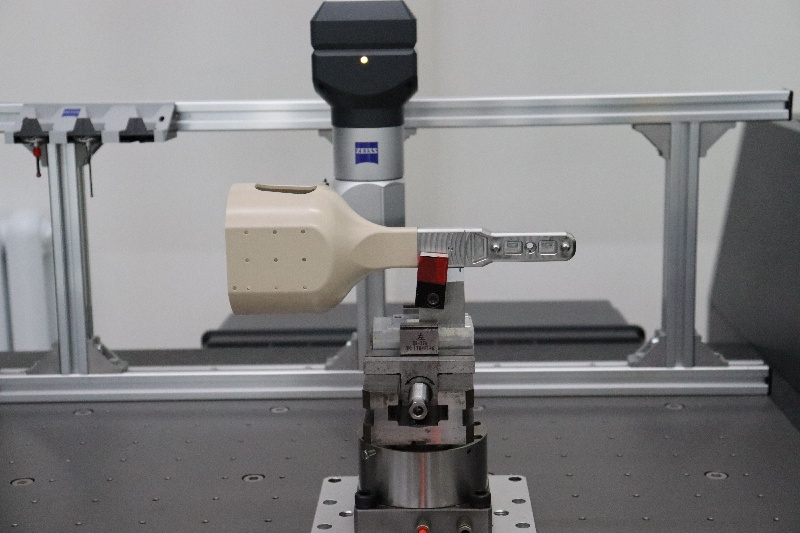
Tolerancias de mecanizado CNC
Es cierto que el mecanizado CNC ha elevado la precisión de fabricación a niveles muy altos. Sin embargo, como ocurre con otros procesos de fabricación, las dimensiones del producto final nunca son perfectas. Y aquí es donde las tolerancias del mecanizado CNC desempeñan un papel fundamental.
Debemos recordar que las tolerancias representan la variación máxima permitida para las mismas dimensiones de dos piezas de la misma serie. Suelen definirse en la fase de diseño.
Hay diferentes aspectos a tener en cuenta a la hora de establecer las tolerancias requeridas:
Componentes de acoplamiento.
Tipo de materiales.
Procesos de fabricación disponibles.
Generalmente es más costoso conseguir tolerancias más estrictas.
Las tolerancias suelen clasificarse según su rigor en los siguientes grupos:
Tolerancias finas.
Tolerancias medias.
Tolerancias gruesas.
Tolerancias muy gruesas.
En general, los límites para cada grupo se establecen en función de normas internacionales, incluidas ANSI B4.1, ANSI B4.2, ISO 286, ISO 1829, ISO 2768, EN 20286 y JIS B 0401.
Para las tolerancias de mecanizado CNC, los límites estándar se encuentran en el rango de ±0,005″ o 0,13 mm. Sin embargo, algunos servicios muy sofisticados afirman ofrecer tolerancias de mecanizado CNC de hasta ±0,0025 mm.
A continuación se muestran algunas tolerancias de mecanizado CNC estándar según el proceso CNC:
Torno — ±0,005″ (0,13 mm)
Fresadora — ± 0,005″ (0,13 mm)
Fresado de 3 ejes: ± 0,005″ (0,13 mm)
Fresado de 5 ejes: ± 0,005″ (0,13 mm)
Grabado — ± 0,005″ (0,13 mm)
Planitud — ± 0,010″ (0,25 mm)
















 SUSCRÍBETE A NUESTRO BOLETÍN
SUSCRÍBETE A NUESTRO BOLETÍN